Outlier or gold nugget? To reduce risk, ensure two (or more) UX research methods derive the same results.
Tackle research questions using multiple perspectives and methods.
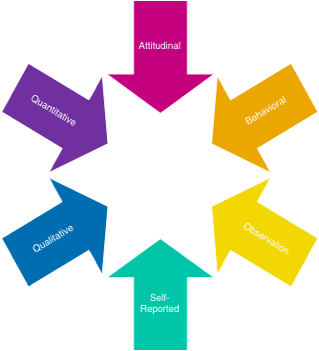
TYPE: Attitudinal or Behavioral
Attitudinal Research
Attitudinal research helps you understand how customers FEEL about a problem, solution, or experience.
Examples: Social Listening, Text Mining, Collage Study
Behavioral Research
Behavioral research helps you understand how customers ACT. What, where, when, and how do customers behave?
Examples: Tree Test, Usability Study, Scroll Map
ROLE: Self-Reported or Observational
Self-Reported Research
In self-reported research, customers report their own attitudes or behaviors. Use caution when choosing self-reported research methods — especially when a question relies on a customer’s (often faulty) memory.
Examples: Survey, Customer Interview
Observational Research
In observational research, researchers see customer behaviors and attitudes first-hand. During usability testing, I can observe a customer’s frustrations just by their facial expressions and don’t need to rely only on what they say.
Examples: Heat Map, Usability Study, Contextual Inquiry
GOAL: Quantitative or Qualitative
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research answers “how many” or “how often.”
Examples: Survey, Web Analytics, Card Sort
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is used to understand underlying reasons, opinions, or motivations. It answers “why” something happens.
Examples: Customer Interview, Diary Study, Ethnography
Related Articles
- Discovering Hidden Insights with Kano Analysis: A Case Study
- ESAT & CSAT: A Survey Alignment Love Story
- UX Research Toolbox: Anatomy of a Compelling Narrative for Your UX Research Reports
- Data Overload? How to Manage the Flow of CX Insights Effectively
- Bias-Free UX Research: Innovative Approaches to Mitigating Bias in the Research Process